What Does SEO Look Like in 2020 [The Basecamp S1E4]

With today’s intense competition to be visible online, SEO has become a critical part of digital marketing. However, like most things that incorporate technology, there are always ongoing changes.
As a digital marketing agency, it’s important for us to not only understand how SEO works to give clients optimal results, but to also keep track of the changes made in Google’s algorithm and how these changes can impact our clients’ business and their visibility online.
SEO is shorthand for Search Engine Optimization and its main role is to make a website more visible. More visibility translates to more traffic and opportunities for you to convert prospects into customers. According to the Digital Marketing Institute, SEO is not only significant because it makes a website more visible, but it also helps to build brand awareness, build relationships with prospects, and assists in positioning a client as an authoritative and trustworthy expert in their field or industry. With SEO being a big part of what we do here at Ascend, here are some trends we think you should look out for in 2020:
Search Engines are Smarter

More and more, Google’s algorithm is rewarding user experience. Algorithms are less keyword focused, and more focused on the user’s experience, their behavior, and their buyer’s journey. Another important feature is user intent. Google is getting smarter in recognizing content and giving users exactly what they are searching for. In the past, content creators would try to game the system by matching their title to whatever the user may search for. However, Google is no longer looking at the title only, but instead matching searches to exactly what the user is searching for.
Optimizing for Mobile
One SEO factor that can’t be ignored in 2020 is optimizing for mobile. Most searches today are done from mobile devices. According to Statista, in 2020, there are 211 million mobile phone search users in the United States, where 95.3% of organic mobile search visits are executed on Google.
Google favors sites that are mobile-first and load quickly, because chances are if a user is searching on mobile, they’re not connected to Wifi. In addition, if pages have a longer load time, the user will likely leave the page, as opposed to sticking around and waiting for the page to load.
Zero-Position Listing
When a user searches for something in Google, the first listing on the results page is referred to as the first position result. One might think you couldn’t rank any higher than that, but in reality, you can. With Position Zero, users are given the information that they are searching for within the Google results page, without the need to click the article. Examples of these are calculators, definitions, maps and featured snippets. Users can find quick results for a review, a recipe, business, or event. If they are still interested in learning more, the link to the content is still provided to them so that they can click and view the page; however, they have gotten a basic overview of the instructions or content without having to dig much further. Here's an example of a featured snippet result from our partner Super-Sod/Soil3 for "How to level your yard."
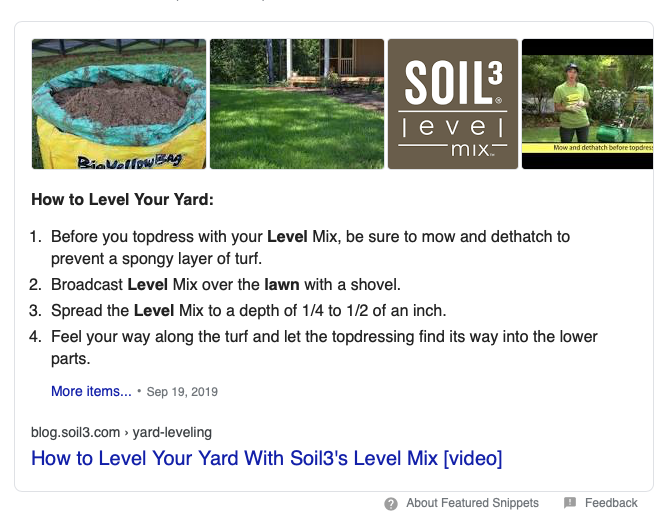
Snippets are automatically created from page content. Snippets are designed to emphasize and preview the page content that best relates to a user’s specific search, meaning that a page might show different snippets for different searches.
Pillar Content
Pillar content is the practice of creating an authoritative presence for your brand or for your company around certain topics. You only want to have a few of these topics, but once you establish what those topics are, you can craft content around those specific topics. To begin, create a pillar page, which is a very long-form page, that consists of in-depth articles with chapters, lots of good visuals, and helpful links that help to establish you as the expert on that particular topic. From there, create more pages or blog posts throughout your site that link back to this authoritative piece of content. In addition, work to ensure that your pillar page is receiving backlinks from external websites to help you build authority and improve your rankings in search results.
Overall, the four features presented focus on user intent and making the user experience is an easy and enjoyable one. When people are searching for information on Google, they don’t want to be sold to, they want to find THE expert and be informed. They want to be the ones to find the answer and get to the bottom of it. And as a business, you have to meet the user where they’re at to sell more.
Here's the video transcript:
Anne Shenton: Welcome to another episode of The Base Camp. I am Anne Shenton, Agency Director here at Ascend Inbound, and I've got John Fuller, web developer extraordinaire. Today we're going to talk about SEO and 2020.
John Fuller: I can pretty much boil it down to it's SEO in 2019 except the search engines are smarter.
Anne Shenton: Okay. And what do you mean by that?
John Fuller: Well, their algorithms have gotten better and they're designed for the end-user so it's less keyword-focused in the algorithm and it's more focused on users' experience, the buyer and their actual behavior, and the buyer's journey, whether it's somebody in the decision phase or somebody in the post-purchase phase.
Anne Shenton: Gotcha. And you've touched on something really important when you talked about user experience and another big term that's being thrown out right now with SEO is user intent.
John Fuller: Yes.
Anne Shenton: A good example of that that I read earlier today was, if you're searching online for a recipe, for example, and you're searching for a quick recipe with kale, and I don't know why you'd ever want to cook anything with kale in it, but if you did, you would want it quickly. And so, if you're searching for quick recipes for kale and you click on the first result, for example, and it shows you that the cook-time is an hour and a half, well that's not a quick recipe, that is bad user intent mapping. Perhaps the person who wrote that article wrote 'quick recipe for kale' in the title of the page to try to get those clicks. Well, Google is getting smarter about that so what it's going to do instead is not necessarily look at people who are just trying to game the system by matching their title to whatever the person is searching for, but actually display the content that has what the user is searching for. So it would show the recipe that actually only took 10 minutes or something like that instead as one of the topics.
John Fuller: Another point to touch on is the user intent is to find it quickly, but they're also, Google knows, most of them are looking on their phone for that kale example, the yummy kale example, they're probably in their kitchen with a bag of kale and they need something quick because they're like me and they're just looking on their phone and they're like, "Man, my spouse told me to cook this. What am I going to do?" That's like fitting into the user, meaning these are where they're at.
Anne Shenton: Right.
John Fuller: And so a big thing for 2020 is to have your website optimized for mobile because most users are on it, especially if it's a B to C company. It's just got to be mobile-first. The whole site's got to be designed mobile-first and that's being taken account for SEO so...
Anne Shenton: Absolutely. Google is definitely giving a favor to sites that are mobile-first, that are loading super-fast, because if you're on a mobile device and you're not somewhere that has wifi, you've got to make sure those pages are loading quickly or else the user's going to leave, they're not going to stick around to wait for the page to load.
John Fuller: Yep.
Anne Shenton: I guess another thing I wanted to mention, and there's a lot. SEO is an entire universe that you can learn more about through Google search. Got really meta her right there. But anyway, another thing that I wanted to talk about too is this idea of the zero position listing.
John Fuller: Explain that more.
Anne Shenton: If you search for something in Google, the first result of the page is the first listing, right? But we want to break it down even further and get to the zero listing. Examples of the zero listing is something that's called a featured snippet. For example, we have a client, Super-Sod, and they have a great example of this right now, how to level your yard, and if you search for how to level your yard in Google search, the instructions for how to level your yard actually show up on the Google results page so they don't have to click into the article, they just see those quick instructions and they see actually a video that shows you how to do it that they can click into right within the results page without having to go to the website. Of course, there is still that link to where if they wanted to learn more they could click in to view the page, but they still get a basic overview of those instructions without having to dig any further.
Anne Shenton: So that's something that you want to make sure you're looking into, making sure that you're optimizing for featured snippets, making sure the architecture of your site, and John can speak to this way better than I could, but it's just coded really cleanly, that's another thing that lends to fast page load times, but it also makes it easier for Google to read the content on those pages as well because Google's just not going to waste any time trying to dig through stuff to get to the answers that their users are looking for in search results.
John Fuller: That's right. Your website has to be a bridge between a machine and the user so it's got to be serving up a data structure that makes sense to a machine, but it's got to be presenting it to the user where it's beneficial for them.
Anne Shenton: For sure.
John Fuller: And that's one of the things that you have to be careful in the way you structure your page, in the way you structure your content, getting technical, the way you structure your bullet lists and your heading tags. It all needs to make semantic sense and it needs to make semantic sense not only for data structure but also for screen readers. One thing that Google is rewarding with SEO and promoting in their algorithms is websites with ADA compliant code. And so that's another big thing in SEO, following what Google's rewarding.
Anne Shenton: Right. 100%. On the same topic of screen readers is optimizing for voice search as well, making sure that you're considering what people might speak into the microphone of their phones to search for quickly instead of actually typing things out. That is only going to become more and more prevalent as people become less reliant on typing and more just, "Tell me the answer right now."
John Fuller: Yeah.
Anne Shenton: Anything else on SEO you want to talk about before we wrap up this episode of The Base Camp?
John Fuller: Pillar content.
Anne Shenton: Okay. Yeah, one of the biggest things we probably should talk about.
John Fuller: Exactly. We saved the best for last.
Anne Shenton: That's true.
John Fuller: That's what we were really doing.
Anne Shenton: That's true. Yeah. So pillar content is this idea around creating an authoritative presence for your brand or for your company around certain topics. You only want to have a few of these topics that you are the authority of for your brand, but once you establish what those topics are, you want to craft content around those specific topics. So what's you're going to do is you'll have a piece of pillar content, so a very long-form page, a very in-depth article with chapters and lots of good visuals and helpful links, and that just establishes you as the expert on that particular topic. And then what you're going to do after that is create a lot of other pages or blog posts throughout your site that link back to this authoritative piece of content. And then, of course, beyond that you want to make sure that that main pillar piece of content is also receiving back links from external websites as well so that you can build up authority for that specific topic or [crosstalk]
John Fuller: And that all goes back to user intent. Just think about when you're using a search engine, you're not looking for a sales pitch, you're looking for an expert.
Anne Shenton: Right.
John Fuller: And that's how Google has orchestrated this and I think it's for the buyer's best interest and, consequently, our best interest as companies. People just want an expert, they want to be informed. They don't want to be sold to.
Anne Shenton: And they want that answer pretty quickly too.
John Fuller: Exactly.
Anne Shenton: Patience is wearing thin in our society.
John Fuller: Exactly.
Anne Shenton: They want to get to that answer. They want to get to the bottom of it. They don't want to cut through any nonsense.
John Fuller: And if you meet the user where they're at you're going to sell more.
Anne Shenton: For sure.
John Fuller: And you're going to succeed.
Anne Shenton: It's the Inbound way.
John Fuller: That's right.
Anne Shenton: All right, well thank you so much for tuning in, guys. This is another episode of The Base Camp and I hope to see you for the next episode.
